本篇文章介紹 Early Stopping 和 Cross Validation 的概念與實作方式。
Early Stopping
為了使訓練的模型不要落入 Overfitting 的情形,可以套用 EarlyStopping 的機制,使訓練過程在達到指定條件時,提前結束。
Keras 提供 Early Stopping 機制的 Callback。可以在 keras/callbacks 下,找到 EarlyStopping 所使用的參數設定與說明。
以下是使用 Keras 實作 EarlyStopping 的範例:
early_stop = EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', min_delta=0, patience=5, verbose=0, mode='auto')
model.fit(train_data, train_label, callbacks=[early_stop])
Cross Validation
在資料學習的領域,通常會訓練模型以估測資料的分類。評斷模型估測的能力時,一般僅對僅對測試資料集進行驗證,其準確度不能完全地代表應用在所有資料上的情形,因此會產生隱性的誤差。
透過交互驗證,能減少驗證時資料集造成的測試誤差。詳細的演算法與解說可參考下文。
K-Fold 演算法 (虛擬碼)
for each fold k
instantiate a neural network
get reference to training data for k
get reference to test data for k
train the neural network
accumulate number wrong, correct
end for
return number (total wrong) / (wrong + correct)
如何取資料
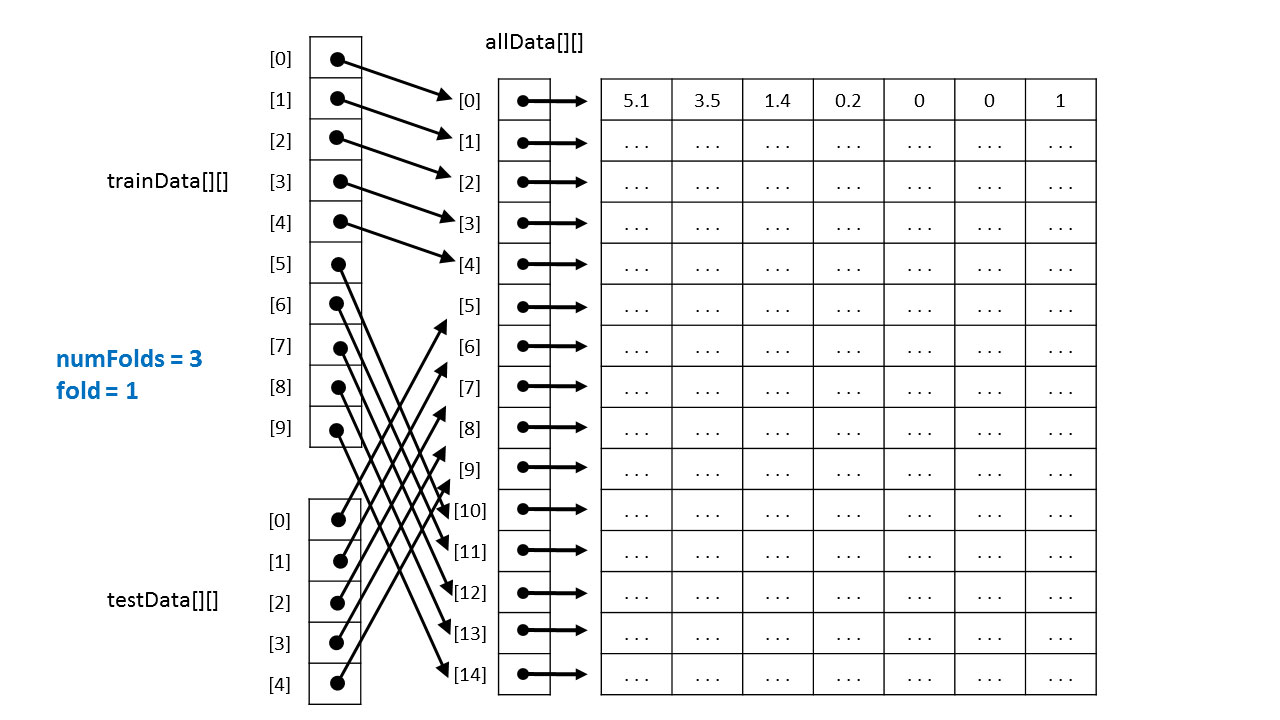
K = 0 時,取出 5 ~ 14 作為訓練資料,0 ~ 4 作為測試資料。
K = 1 時,取出 0 ~ 4, 10 ~ 14 作為訓練資料,5 ~ 9 作為測試資料。
K = 2 時,取出 0 ~ 9 作為訓練資料,10 ~ 14 作為測試資料。
在 Sci-kit Learn 中使用 K-Fold
可以使用 sklearn.model_selection.StratifiedKFold 類別,引用 K-Fold 演算法進行交互驗證。
可以使用的參數包含 n_splits, shuffle, random_state 三個參數,其中 n_splits 表示 Fold 測試的次數,而 shuffle 參數則決定在擷取測試資料時是否隨機抽取,random_state 則可填入隨機種子,用於決定最後隨機抽取的結果。
然而使用 shuffle 參數僅改變抽取的資料索引,索引的順序不會被改變。因此還是需要在訓練時對資料再進行 shuffle ,以增加神經網路的收斂效果。可參考以下範例:
>>> from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
>>> import numpy as np
>>> X = np.ones(10)
>>> y = [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
>>> skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3)
>>> for train, test in skf.split(X, y):
... print("%s %s" % (train, test))
...
[2 3 6 7 8 9] [0 1 4 5]
[0 1 3 4 5 8 9] [2 6 7]
[0 1 2 4 5 6 7] [3 8 9]
>>> skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=True)
>>> for train, test in skf.split(X, y):
... print("%s %s" % (train, test))
...
[2 3 4 5 8 9] [0 1 6 7]
[0 1 3 5 6 7 9] [2 4 8]
[0 1 2 4 6 7 8] [3 5 9]
